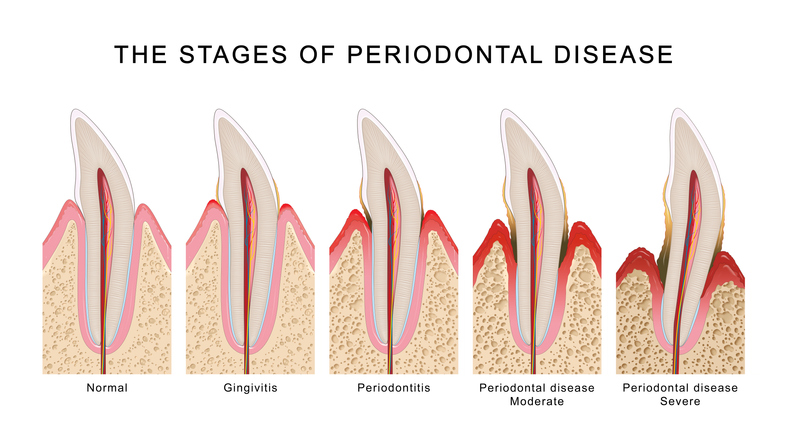
The most common forms of Periodontitis are:
- Occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy
- Common features include rapid attachment loss, bone destruction, and familial aggregation (more cases of a given disorder in close relatives of a person with the disorder than in control families)